Leave Your Message
Solenoid Directional Control Valves play a pivotal role in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, serving as essential components that manage the flow of fluids in various applications. These valves utilize electromagnetic mechanisms to control the direction and pressure of fluid flow, making them indispensable for automated systems in manufacturing, automotive, and robotics industries. Understanding how solenoid directional control valves work is crucial for engineers and technicians who seek to optimize system performance and enhance operational efficiency.
The operation of solenoid directional control valves is based on the principles of electromagnetism, where an electric current generates a magnetic field that actuates the valve mechanism. This allows for precise control over the fluid pathways, enabling the system to perform complex tasks with reliability. By manipulating the flow direction, these valves facilitate critical processes such as actuation, cycling, and safety measures in machinery. As we delve deeper into the mechanics and functionalities of solenoid directional control valves, it becomes clear how these components contribute to the seamless operation of modern automated systems.
A solenoid directional control valve is a crucial component in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, designed to control the flow and direction of fluids. Its primary function is to facilitate or restrict movement within machinery by directing fluid towards specific pathways, thereby enabling precise control over actuation mechanisms. The solenoid aspect refers to an electromagnetic coil that converts electrical energy into mechanical action, allowing for remote operation of the valve.
When an electrical signal is applied to the solenoid, it creates a magnetic field that moves a plunger within the valve, opening or closing fluid passageways. This action changes the path of the fluid flow, which can be used to start, stop, or change the movement of actuators such as cylinders or motors. The quick response time and reliability of solenoid directional control valves make them an essential choice in various applications, ranging from industrial automation to robotics, where precise control over fluid movement is critical for optimal performance and efficiency.
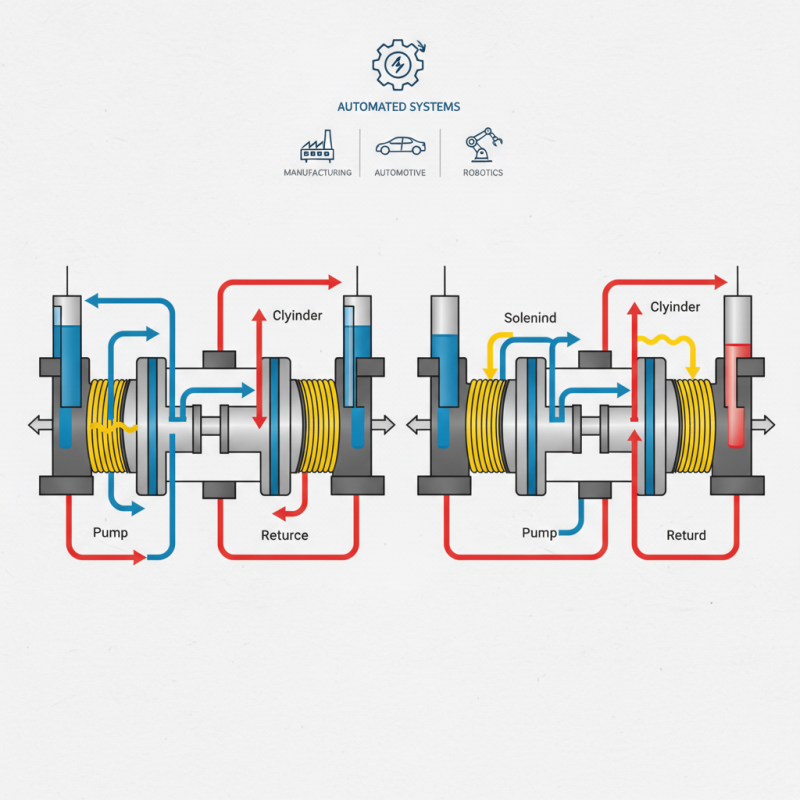
A solenoid directional control valve is an essential component in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, designed to control the flow of fluid or air by directing it to different paths. Understanding its components is crucial for grasping how it functions effectively in various applications. The primary elements of a solenoid directional control valve include the solenoid, spool, spring, and body.
The solenoid is an electromagnetic device that converts electrical energy into mechanical movement. When energized, it generates a magnetic field that pulls or pushes the spool within the valve body. The spool, typically cylindrical, has multiple flow paths created in its design that can align with the inlet and outlet ports on the valve body. By moving the spool in response to the solenoid's action, the valve can switch the flow direction of the fluid or air, enabling the operation of actuators, cylinders, or other devices in the system.
Additionally, the spring plays a critical role in the operation of the valve. It returns the spool to its neutral position when the solenoid is deactivated, ensuring that the valve does not remain stuck in one position, which could disrupt flow control and system functionality. Together, these components work harmoniously to provide precise control over fluid flow, making solenoid directional control valves vital in manufacturing, automation, and various industrial tasks.
A solenoid directional control valve is an essential component in hydraulic and pneumatic systems, enabling precise control of fluid flow. The operation of a solenoid directional control valve is fundamentally based on electromagnetic principles. When an electric current passes through the solenoid coil, it generates a magnetic field that moves the plunger or armature within the valve. This movement changes the position of internal spools or plates, allowing or blocking the passage of fluid. According to industry reports, such as those from the International Fluid Power Society, solenoid valves can achieve operational response times as low as 20 milliseconds, making them ideal for applications requiring quick actuation.
Furthermore, the versatility of solenoid directional control valves is evident in their ability to manage multiple flow paths with just one device. Commonly available in configurations like 2/2 or 5/2, these valves can effectively route fluid in various directions depending on the system's requirements. Data from the Fluid Power Market Report indicates that the global market for solenoid valves is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.2% from 2021 to 2026, reflecting their significance in automation and control applications. By controlling flow direction and volume, solenoid valves not only enhance system efficiency but also contribute to improved energy management within industrial processes.
Solenoid directional control valves play a crucial role in various industrial applications, primarily in controlling the flow of fluids and directing the movement of actuators. These valves are commonly used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems to manage the operation of machinery, ensuring precise control over processes. For example, in manufacturing settings, solenoid valves can efficiently manage the movement of robotic arms or conveyor belts, facilitating automation and enhancing productivity.
In the construction industry, solenoid directional control valves are vital for operating heavy equipment such as excavators and cranes. They help manage hydraulic systems that require precise flow control for lifting and moving materials. Additionally, in the automotive sector, these valves are employed in assembly lines to regulate the movement of components during production. Their reliability and efficiency contribute significantly to minimizing downtime and improving operational effectiveness across various industrial environments.
| Application | Function | Operating Pressure (bar) | Typical Fluids | Response Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive Steering Systems | Control fluid flow to adjust steering angle | 20-200 | Hydraulic oil | 20 |
| Industrial Automation | Control the actuation of cylinders and actuators | 10-300 | Compressed air, hydraulic fluid | 25 |
| Agricultural Equipment | Regulate the flow of liquids in sprayers | 5-50 | Fertilizer solution, water | 30 |
| HVAC Systems | Control heating and cooling fluid distribution | 1-10 | Water, refrigerant | 50 |
| Robotics | Manage precision movement of robotic arms | 15-250 | Hydraulic fluid | 15 |
Solenoid directional control valves play a crucial role in enhancing fluid control systems across various applications. One of the primary benefits of utilizing these valves is their ability to provide precise control over the flow and direction of fluids. By using electromagnetic coils to activate the valve mechanism, solenoid valves ensure quick and reliable switching between different flow paths. This capability not only improves operational efficiency but also allows for the automation of processes, reducing the need for manual intervention in fluid management.
Another significant advantage is their versatility in various environments. Solenoid directional control valves can be designed to handle different types of fluids, including oil, water, and air, making them suitable for diverse industrial applications such as hydraulic systems, pneumatic controls, and even in the automotive sector. Their compact design also facilitates installation in tight spaces, contributing to streamlined system designs. Furthermore, these valves typically feature a robust construction, which enhances durability and reliability, ensuring prolonged operational lifespans in demanding conditions. Overall, the integration of solenoid directional control valves into fluid control systems brings forth improved performance, efficiency, and adaptability.